Abstract of the TELS GLOBAL Marketing Department’s report to the Board of Directors
General Trends in the Global Market
Unfortunately, almost all the negative trends that started two years ago continue to develop. The escalation of political and military confrontation along the Russia-Ukraine line is intensifying, joined by a significant increase in tensions in the Middle East and the growing terrorist threat around the world. A global collapse of the international relations system is taking place, which demands a shift in the paradigm of thinking from people and business: it is necessary to abandon hopes for a return to the previous state in the coming decades and accept the fact that the former international law is no longer effective, and the new one will be formed based on the results of the forceful repartition of the world.
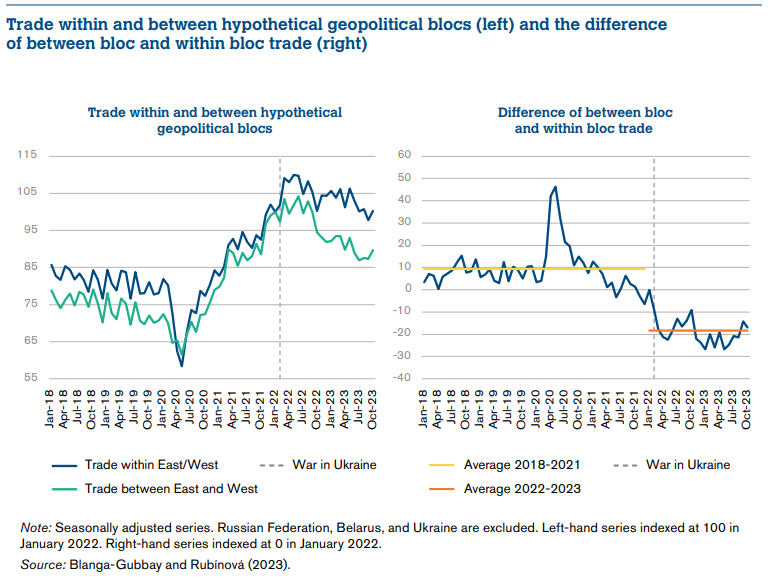
International trade will be increasingly trapped in regional and political blocks. Import substitution in key security matters (food, technology) will become a priority idea of the countries’ economic architecture. This will create conditions for the development of domestic industries, but it does not necessarily imply an improvement in the living standards of the population. One should realize that in the near future humanity will not enjoy a life as good as it did in the period between 2000 and 2018. The globalism that made it possible to reduce the cost of goods and exchange them easily is over. There are no more reliable means of storing and accumulating resources: electronic assets are becoming extremely vulnerable – they can be blocked by operators or become the target of cybercrime, especially with the development of technology (AI for hacking, deepfake, etc.).
These are the general conclusions a business should draw in the current environment:
1. To expedite the expansion of presence in the domestic markets of large countries (unions) and “friendly blocks”. Blocks are unstable formations with floating boundaries, sometimes based on political, but more often on social and cultural criteria, indicatively:
- West – the USA, Canada, the UK, the EU, and satellites;
- China, Russia, and other states with traditionalist culture (e.g., Brazil, Argentina, Azerbaijan, etc.);
- Islamic countries of the Middle East.
- Separate interblock countries are likely to be Turkey, India, Kazakhstan, and other countries capable of balancing policies, if the conditions allow.
2. To structure offices in different countries/blocks (especially opposing ones) and organize their development as independent national entities that will be perceived by the locals as their own and not “aliens”.
3. To prioritize material accumulation in resource matters (sometimes it is better to increase important material stocks than to invest in deposits).
4. At the same time, it is important to retain and develop professional capacity in the global trade issues: even though the demand for such services will decrease, it will not disappear, and such services will cost more.
European Union
The EU is facing a crisis on many levels, including political and economic, which are interconnected. The shocks from the loss of cheap Russian energy resources have not yet been overcome, and their consequences are growing, which is reflected in the continuing decline in production activity and lower living standards of the population. Domestic and foreign trade markets are contracting, PMIs for the industrial sector in Europe’s largest economies have been negative since 2022, and there are no drivers for a sustainable transition into the positive zone (above 50 points) yet. The PMI for the Euro zone dropped to 46.1 points in March, -0.4 points compared to February.
At the same time, the EU transportation industry is facing pricing pressure due to the rising rates. The main cost drivers are personnel costs, operating costs, energy and insurance costs, etc. The increase in the road toll rates in Germany also has an impact. The European Freight Association of International Freight Forwarders (ELVIS) AG has warned that the current decline in the overall truck mileage, together with the current excess of freight capacity and the expected drop in sales, is leading to a shrinking truck fleet; its volumes will no longer be available on short notice if the market begins to recover. As a result of this process, a sharp rise in the spot market prices and a shortage of cargo capacity may occur.
The divisive trends between Europe and the South-East are developing, which is connected both with the political escalation between the US and China (and Europe is a US ally here), and the increasing complexity/expensiveness of logistics as a result of the refusal to use transit through Russia for political reasons and through the Suez Canal due to the military escalation in the region. The southern transportation corridor, even with its rapid development in the next five years, will not compensate for the lost capacity of traditional routes. (However, according to Russian Railways, trans-Russian transit from China to the EU is recovering and has almost returned to the 2021 level in the first quarter of 2024).
It is likely that in a calmer foreign policy environment, the EU economy could stabilize in a couple of years, but the global tensions are not allowing this to happen. More defense spending is still expected ahead in the face of high production costs. Almost all analytical financial institutions expect a slowdown in the growth of the Euro zone economy in 2024 (in particular, the S&P rating agency forecasts a 0.7% growth of the EU’s GDP in 2024). There are doubts that the recovery in the economic growth will be significant beyond 2024, as well.
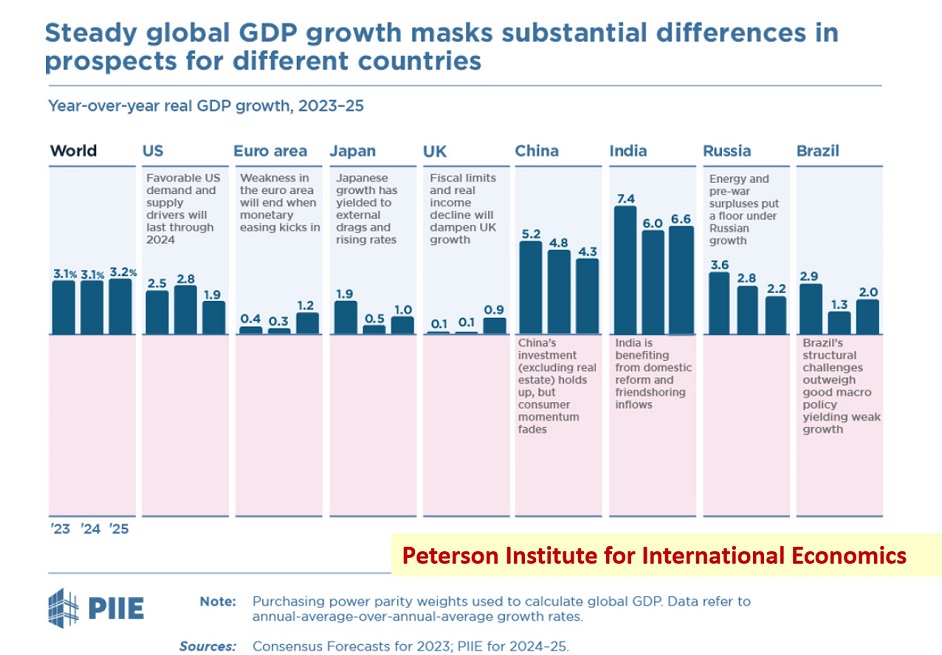
That said, the EU economy still constitutes about one-sixth of the global GDP. The EU’s internal market relies on the high capacity gained over decades due to advanced technologies that create high added value. This is the resource for maintaining the sustainability of the social and political basis, industrial and consumer demand. This safety buffer is supporting the region’s business prospects, although the current and short-term conditions will be unfavorable.